Carry Trade Strategy
Carry Trade Strategy
Carry trade is a Forex trading strategy that involves borrowing money at a low interest rate and investing it in assets with higher returns.
Explaining Carry Trade
Currency carry trade is a strategy that involves selling a currency with a relatively low interest rate while simultaneously buying a currency with a relatively high interest rate. Forex carry traders aim to capture the interest rate differential between two currencies, which can be significant depending on the leverage they use.
- Investors borrow in a low-interest-rate currency and invest in a higher-interest-rate currency, profiting from the interest rate differential (the "carry") between the two.
Typically, investors borrow money in Japanese yen or Swiss francs, two currencies that traditionally offer very low interest rates, close to zero. They then use these funds to open long positions in currencies with higher interest rates, such as the Canadian Dollar, New Zealand Dollar, and Australian Dollar.
About Interest Rates
Interest rates have a powerful impact on the Foreign Exchange market. Any rate change by one of the eight major global central banks can disrupt the Forex market, with surprise changes having an even greater effect.
Interest rate adjustments respond to new economic conditions, and every policy aims to stabilize the economy. Interest rate policies serve two main purposes: to stimulate growth or to reduce inflation.
(i) Decreasing interest rates aims to boost growth and lower unemployment.
(ii) Increasing interest rates aims to reduce inflation.
Interest rates move in trends because the economy cycles through periods of growth and contraction, moving upward and then backward. As shown in the table below, major central banks implement different interest rate policies because monetary authorities have varying goals, and each economy has its own unique characteristics. Japan and Switzerland traditionally offer low interest rates.
Table: World Interest Rates (source: TradingEconomics.com)
| World's Major Central Banks and their Interest Rate Policies (at the time of the post) | |||
| Country | Last | Previous | Reference |
| Switzerland | 0.00% | 0.25% | 6/25/2025 |
| Japan | 0.50% | 0.50% | 6/25/2025 |
| Singapore | 1.43% | 1.56% | 7/25/2025 |
| Euro Area | 2.15% | 2.40% | 6/25/2025 |
| South Korea | 2.50% | 2.50% | 6/25/2025 |
| Canada | 2.75% | 2.75% | 6/25/2025 |
| China | 3.00% | 3.00% | 6/25/2025 |
| Australia | 3.85% | 3.85% | 6/25/2025 |
| United Kingdom | 4.25% | 4.25% | 6/25/2025 |
| United States | 4.50% | 4.50% | 6/25/2025 |
| Saudi Arabia | 5.00% | 5.00% | 6/25/2025 |
| India | 5.50% | 6.00% | 6/25/2025 |
| Indonesia | 5.50% | 5.50% | 6/25/2025 |
| South Africa | 7.25% | 7.50% | 5/25/2025 |
| Mexico | 8.00% | 8.50% | 6/25/2025 |
| Brazil | 15.00% | 14.75% | 6/25/2025 |
| Russia | 20.00% | 21.00% | 6/25/2025 |
| Argentina | 29.00% | 29.00% | 5/25/2025 |
| Turkey | 46.00% | 46.00% | 6/25/2025 |
Carry Trade Strategy
A carry trade strategy involves selling a low-interest-rate currency and buying a high-interest-rate currency. It is one of the most successful Forex trading strategies.
The Overnight Rate
Carry traders earn an interest rate differential every day of the year at midnight (based on your broker’s time server).
This interest rate differential is called the Rollover Rate, Overnight Rate, or Swap Rate. On Wednesdays, this Overnight Rate is tripled to cover the missed rates for Saturday and Sunday.
Popular Carry Trade Forex Pairs
The New Zealand Dollar and Australian Dollar offer the highest interest rate yields, while the Japanese Yen and Swiss Franc offer the lowest. This is why pairs like AUD/JPY and NZD/JPY are among the most traded by Forex carry traders.
The Japanese Yen and its Correlation with US Stocks
The Japanese Yen has traditionally been used as a borrowing currency by equity traders worldwide. These traders borrow in Japanese Yen, which has near-zero interest rates, and buy US stocks with long-term bullish trends or high dividend yields. This practice has created a strong correlation between the JPY market and the stock market. In the following USDJPY and Dow Jones charts, you can see this intermarket correlation as an extreme example of closely linked trading.
Chart: USDJPY and Dow Jones Correlation

Practical Examples:
- Common funding currencies include JPY, CHF, EUR (when ECB rates are low), and sometimes USD, depending on Federal Reserve policy.
- Popular target currencies are AUD, NZD, South African Rand (ZAR), Turkish Lira (TRY - very risky), Brazilian Real (BRL), Mexican Peso (MXN), and other emerging market currencies.
Carry trade unwinds play a major role in Forex volatility during crises. When traders rush to exit, selling target currencies and buying back funding currencies, it accelerates the decline of high-yield currencies and the rise of funding currencies.
Calculate Interest Rate Earnings
The daily interest for each Forex currency is calculated as follows:
■ (Interest Rate of the Long Currency – Interest Rate of the Short Currency) × Position Size
Example
For a long position of NZD/USD of 5 standard lots, the daily earnings are calculated as:
■ (0.0250 – 0.005) × 100,000 × 5 = 10,000 USD ÷ 365
This equals approximately $27.37 per day.
Note that brokers may use slightly different overnight rates.
Carry Trade Strategy and Its Major Risks
- Currency Risk:
This is the most significant danger. If the currency you’re invested in loses value sharply against the one you borrowed, your losses can far outweigh the interest earned.
For example, if the AUD drops 10% against the JPY, any 4.25% interest gain is wiped out multiple times.
- Sudden Volatility:
Events like the 2008 financial crisis or the COVID panic cause investors to quickly exit risky positions and high-yield currencies—a process known as “unwinding” carry trades. During these periods, safe-haven currencies such as JPY, CHF, and USD often surge, leading to large losses for carry traders.
- Interest Rate Shifts:
If the interest rate on the currency you borrowed increases or the rate on the currency you hold decreases, the profit margin shrinks, lowering returns.
- Leverage Risks:
Using high leverage means even small adverse price moves can cause big losses or trigger margin calls.
- Liquidity Problems:
During market stress, it can be difficult to close large positions quickly without facing steep price slippage.
Important Factors Affecting Carry Trade
Here are some key points for successful Currency Carry Trading:
(1) Leverage Your Positions Wisely
In the previous AUDUSD carry trade example, a long position of 500,000 USD (5 lots) can generate about 10,000 USD annually. Carry traders can open 5 lots with only a 5,000 USD account, which means 100:1 leverage. If everything goes well, this could yield 200% returns in one year. However, the risk is enormous—using 5,000 USD margin for a 5-lot position can easily wipe out your account. Successful carry trading means avoiding greed and using leverage between 2:1, 5:1, and up to 10:1. This results in lower returns but significantly reduces risk.
(2) Interest Rate Forecast
If central banks plan to raise their domestic interest rates, it can create great opportunities for carry trade. Money tends to flow toward higher yields, and carry traders seek not only interest rate differentials but also potential capital appreciation. Before opening carry trade positions, thoroughly research the expected interest rate policies of the two central banks involved.
(3) The Volatility Factor
Carry trade performs better in low-volatility environments. Traders prefer low-risk conditions for their investments. High volatility combined with high leverage is very dangerous for carry traders.
(4) The Role of Technical Analysis
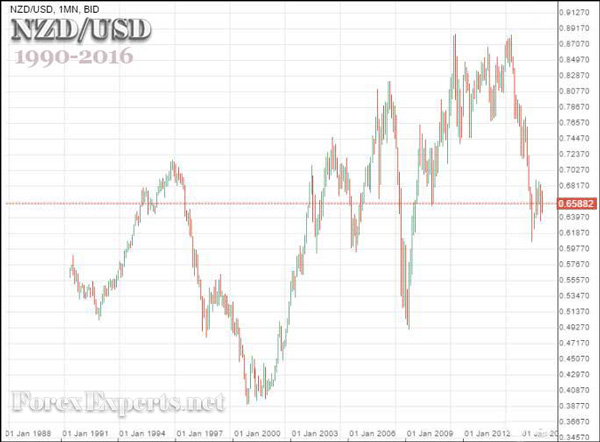
Some traders think technical analysis doesn’t apply to carry trade, but they’re wrong. For example, if you want to go long on NZDUSD after it moved from 0.50 to 0.85 (as it did between 2008 and 2011), but the pair typically cycles between 0.40 and 0.88, that decision could be disastrous. Avoid going long on currencies that have already exhausted their upward potential and are likely to move downward soon.
Chart: NZDUSD
(5) The Extended Role of Central Banks
If a carry trader is long on the currency of an exporting country, they face the risk of central bank intervention. When that currency appreciates significantly, the central bank is likely to act to prevent further gains, which can reverse the profits from carry trade.
(6) Carry Trade through a Basket of Pairs
Trading a basket of pairs instead of a single pair can greatly reduce risk exposure. For example, instead of going long only on AUDJPY, you might also go long on NZDJPY. Carry traders can also use a more advanced strategy by trading a full basket of currencies, combining the three highest-yielding and three lowest-yielding Forex currencies. This method is commonly used by professional carry traders like investment banks.
■ Currency Carry Trade Strategy
ForexExperts.net